Chainlink - Solving the Oracle Problem

The Problem
Imagine you are programming a smart contract on the Ethereum blockchain, replicating a real-world bet. You and a friend decide to bet on the outcome of a football (soccer) match. Your friend is sure: Bayern Munich will win the Champions League final of 2021. However, you believe that they will not succeed, as it is unlikely that they will win twice in a row. You are willing to bet $100 of your funds on your opinion.
Programming a smart contract for this bet seems like a good idea at first. Both participants deposit $100 into the smart contract. If Bayern Munich wins the Champions League final, the total $200 are transferred to your friend; if Bayern Munich loses, you receive the $200. No problem, right?
Not so fast. How does the smart contract know the result of the match? It could work like this: Another friend of yours acts as a referee, who will collect the match's outcome and feed the smart contract with it. But there's a problem. There's always a possibility of manipulation. Your friend could pay the referee to decide in his/her favor. There needs to be a way to inject data onto the blockchain without relying on trusted third parties. That's where Chainlink comes in.
Level up your DeFi knowledge and subscribe to the newsletter!
How Chainlink works
Chainlink is an oracle network that collects real-world data (like football matches) and provides them to smart contracts on the blockchain. $LINK is the native asset on the network to pay for services.
The process starts when smart contracts require data from the outside world. The Chainlink network recognizes this as an event and creates another smart contract on the blockchain called the Chainlink Service Level Agreement (SLA) Contract. The SLA contract then makes three different contracts:
Chainlink Reputation Contract
This contract checks whether or not the oracle provider has a legit track record. If not, the contract does not consider unreliable nodes further.
Chainlink Order-Matching Contract
This contract matches the information request with reliable Chainlink nodes. It first selects the right number of nodes sufficient to execute the task and then decides which nodes are reliable enough to do so. This is the case if the requesting contract doesn't choose the nodes itself.
Chainlink Aggregation Contract
The Chainlink Aggregation Contract checks whether the given information by the nodes is accurate or not.
After that, the request is translated into a language that off-chain sources can understand, which is then transferred to an off-chain data collection source. The Aggregation Contract then collects the data from one OR multiple sources and checks it for accuracy.

So if ten nodes tell the right answer, how the football match ended, and one node has false information, the Aggregation Contract can tell that this particular node provides inaccurate information, which is then discarded.
That is how Chainlink can provide a reliable way for smart contracts to collect off-chain data.
Tokenomics
The Requesting Contract holder pays the Chainlink nodes for their services with $LINK, the native asset of the Chainlink network. The price of the services is determined by supply and demand.
Chainlink node operators also stake $LINK to set up their nodes in the first place. This concept ensures that the node providers are trustworthy. The more $LINK a node stakes, the more likely the Chainlink Reputation Contract will choose it.
The demand for $LINK is, therefore, highly tight to the usage of the platform. The more nodes are involved with Chainlink, the higher demand for $LINK, the higher the price.
Usage of the platform
Chainlink is the most used oracle solution today. Most DeFi projects on the Ethereum blockchain today use their services. Projects like Synthetix, DMM, Aave, bZx, Ampleforth, Loopring, Set Protocol, Nexus Mutual, and many more officially partnered with Chainlink.
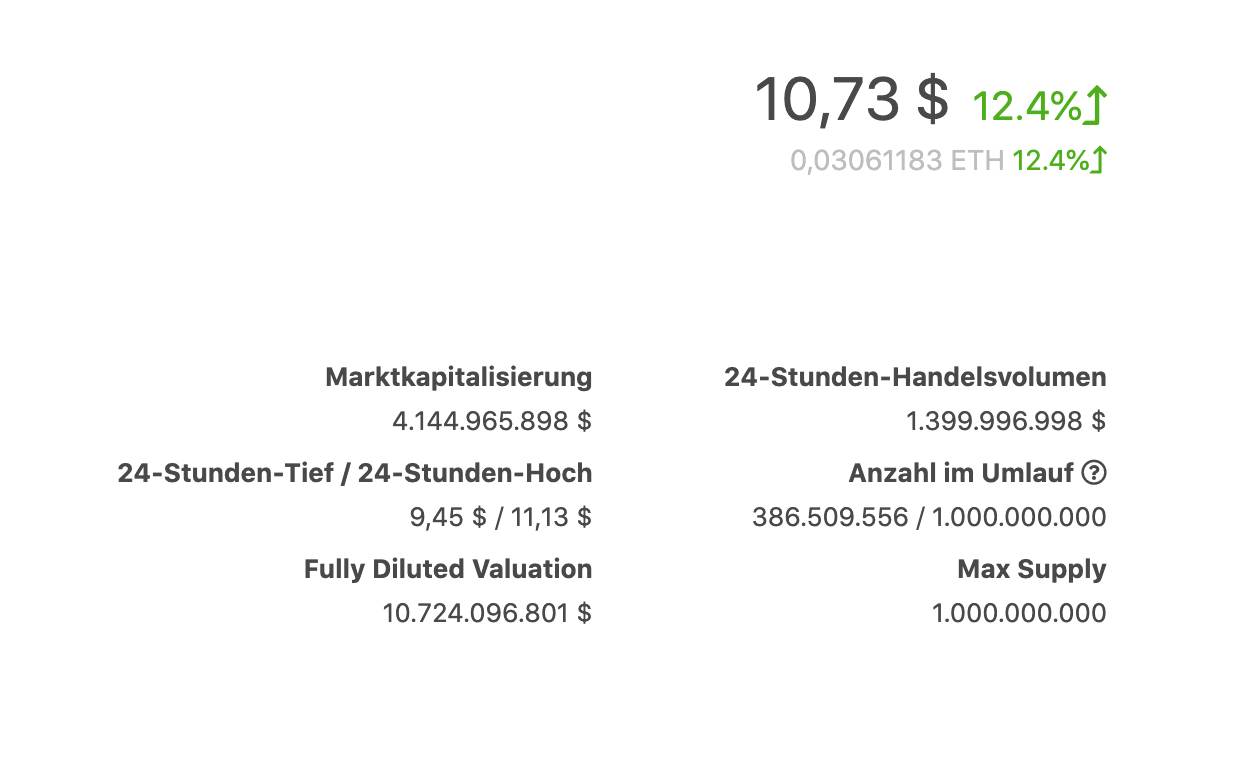
Today, $LINK is in the top five cryptocurrencies on CoinGecko, which is an indicator that the platform is used heavily.
Conclusion
Chainlink is one of the hottest DeFi projects right now because it solves one of the fundamental problems in the blockchain space. How can we get reliable off-chain data onto the blockchain? Chainlink has the answer.
But is $LINK worth buying? The price of $LINK is highly tight to the usage of the platform. The more projects integrate Chainlink services as an oracle solution, the more demand for $LINK, the higher the price. So if you truly believe that this is happening more and more in the future, $LINK might be a good buy right now.
But be careful. It is not a hidden gem. Many people are aware of the project, and currently, the fully diluted valuation is at $10 billion.
In the end, only you can make the decision.

All information presented above is for educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice.