AVALANCHE - How the Future of the Internet Looks Like
The Problem
Unfortunately, DeFi applications are costly. Most DeFi applications are still running on Ethereum. Even though ETH 2.0 will probably go live in December 2020, it will take several years until Ethereum is fully scalable.
By scalable, we mean that thousands of transactions per second are possible. For comparison: Visa processes about 2000 transactions per second. To keep up with this, Ethereum will need Sharding.
However, there is already an enormous demand for Decentralized Finance TODAY. And not only that. We are probably facing the biggest bull market in the history of financial markets. Perhaps the next crypto bubble could be as big as the 2000s internet euphoria.
That is why we need scaling blockchains. Not tomorrow. Not today. We need blockchains that can not only map transactions but can also support entire financial applications. Ethereum will reach its limits in the course of the next bull market, but what will move up?
We at DEFI TIMES believe that this will help a variety of new blockchains to gain reach. We want to introduce one of them today: Avalanche.
How does Avalanche work in general, and how does the new protocol differ from existing blockchains like Ethereum?
Level up your DeFi knowledge and subscribe to our newsletter!
How Avalanche works
The Avalanche Blockchain allows many more transactions than established blockchains, like Bitcoin. While Bitcoin only processes about seven transactions per second, the Avalanche Blockchain can validate about 4500 transactions per second. This is more than Visa currently validates.


However, the Avalanche Blockchain is mainly built for DeFi applications. That means for lending, borrowing, exchanges, etc. For this purpose, there are so-called subnetworks. Every application running on the Avalanche Blockchain has its subnetwork. This subnetwork is entirely customizable and can be built using a toolkit. This is a big difference to Ethereum, where every application is calculated on the main chain.
Ultimately, this would lead to many different subnetworks, which are all compatible with each other, which means that you can transfer tokens and assets from one subnet to another without any restrictions.
Different consensus mechanisms
There are two different consensus mechanisms on the Avalanche Blockchain: Avalanche and Snowman. The Exchange Chain (we will come to this later) is based on the so-called Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG). This is closely related to the way IOTA works. Snowman, on the other hand, is mainly used for smart contract applications.
Primary network
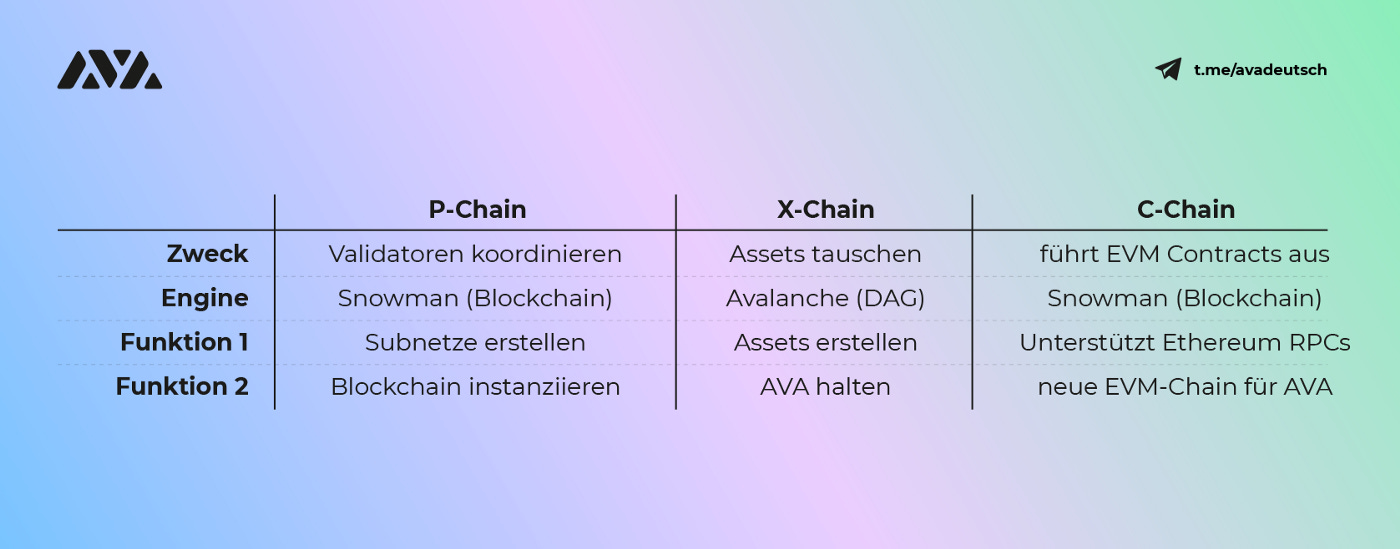
The primary network is separated from the subnets. It consists of 3 chains: the Platform Chain, the Exchange Chain, and the Contracts Chain. The Platform Chain and the Contracts Chain are based on the Avalanche Consensus Protocol, while the Contracts Chain is based on the Snowman Consensus Protocol.
By default, the Contracts Chain is responsible for creating smart contracts compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). The Exchange Chain enables the creation of assets and the transfer of assets between the different subnets. The Platform Chain coordinates the validators.
Tokenomics
AVAX is the native token on the Avalanche Blockchain and has many different use-cases. This token is used for staking, which generates the security of the blockchain. However, it is also used to pay the transaction fees that arise from the blockchain's use.
When participants stake their AVAX, they are rewarded with a payout (inflation). The more tokens you stake, the bigger the reward. The staking duration also plays a role in the payout's size because the longer a participant stakes his funds, the more tokens he receives.
AVAX has a limited token supply of 720 million tokens. However, this amount is not final since AVAX is a deflationary token. The transaction fees are used to burn AVAX and not to pay the validators. Therefore in practice, there will be less than 720 million tokens.
Unique Selling Point
Avalanche is fundamentally different from all other blockchains. The fundamental difference is the Avalanche Consensus Protocol. Established blockchains like Bitcoin still work with the Nakamoto Consensus Protocol. Also, the Ethereum blockchain will not get away from it either for quite some time. This prevents the blockchain from scaling because it becomes more and more expensive to use over time. Therefore, more and more blockchains have been created, making trade-offs in the blockchain trilemma: Decentralization, speed, or security. EOS, for example, exchanges decentralization for speed.
The Avalanche Consensus is a cryptographic breakthrough that solves the trilemma for the first time in blockchain history because its blockchain is decentralized, fast, and very secure. The Avalanche Consensus mechanism seems to be the only solution for the blockchain trilemma so far.
Summary
Avalanche promises to solve one of the fundamental problems in the DeFi industry: scalability. The solution is ingenious: Applications are distributed on different subnetworks (subordinate blockchains), which make DeFi applications faster and guarantee the security of the blockchain. The speed of the Avalanche Blockchain is mainly due to the Snowman consensus algorithm.
AVAX token holders benefit from the usage of the blockchain. The more the blockchain is used, the more transcription fees are paid, the more tokens are burnt.
You should only buy the token if you want to use the Avalanche blockchain or bet on the increased usage of the blockchain.
We at DEFI TIMES believe that Avalanche has a good chance of cutting a piece of the DeFi pie. In times of high ETH gas prices, cheap and fast transactions will experience increasing demand. Therefore, it may well be that more and more Ethereum projects will migrate to the Avalanche blockchain, mainly because the subnets are EVM-compatible.
All in all, we think Avalanche is worth keeping an eye on. If you want to learn more about Avalanche, visit their website, or follow them on Twitter!
All information presented above is meant for informational purposes only and should not be treated as financial, legal, or tax advice. This article's content solely reflects the opinion of the writer, who is not a financial advisor.
Do your own research before you purchase cryptocurrencies. Any cryptocurrency can go down in value. Holding cryptocurrencies is risky.